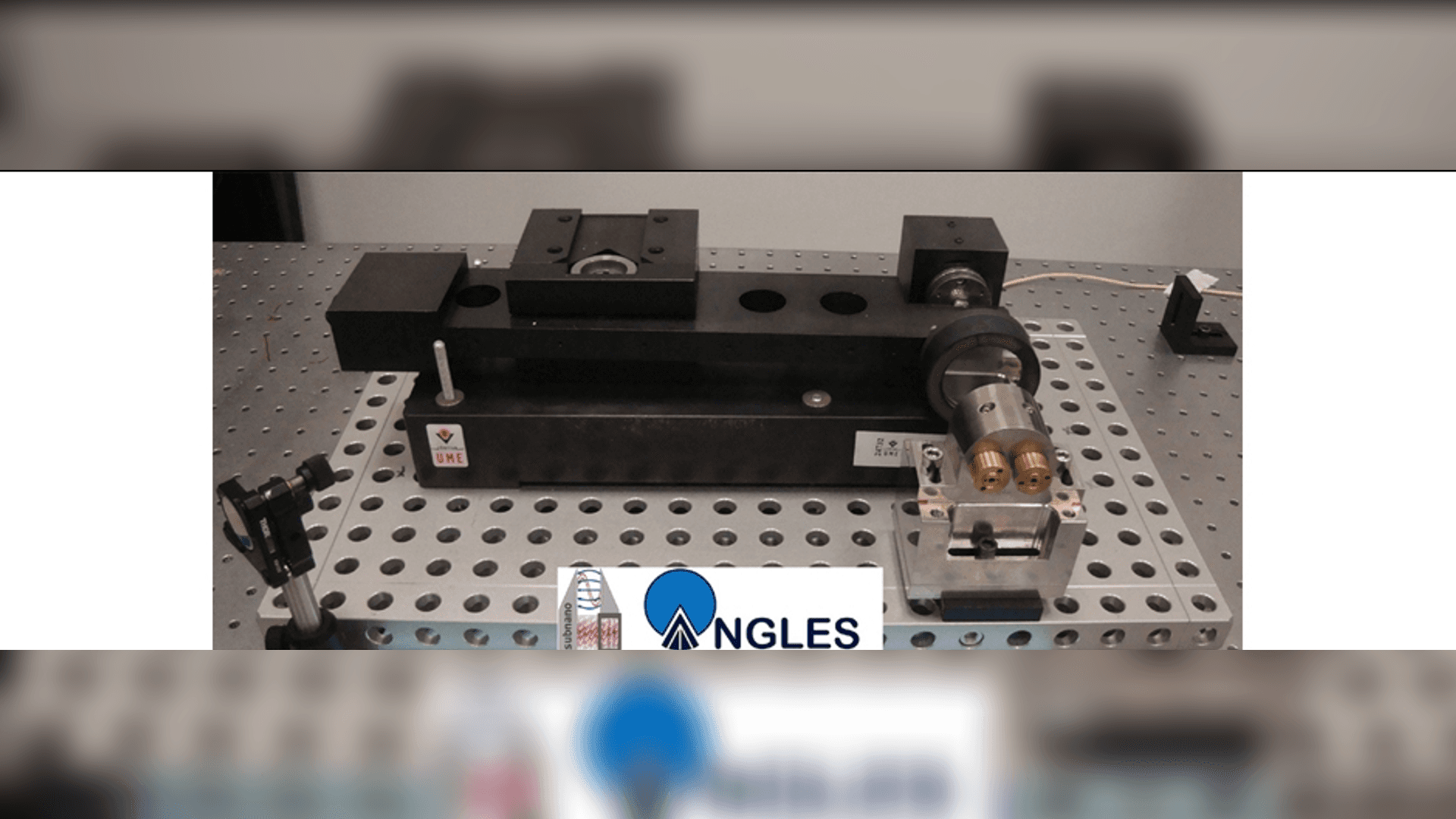
TÜBİTAK UME measured interatomic distances in picometers (one trillionth of a meter) and angles in 1 nanoradian steps produced by the small angle generator it developed with picoradian (one trillionth of a radians) precision; with the Differential Fabry-Perot Interferometer (DFPI) developed within the scope of EU Framework Programs Projects.
In the frequency-based angle measurement method developed by utilizing the frequency-based measurement advantages of DFPI and the stable measurements of the high-precision angle generator, DFPI was used for nanoradian angle measurements for the first time.
In the NANOTRACE European Union Project between 2008 and 2011, displacement measurements with a sensitivity 100 times smaller than the atomic size (picometer), which have important potential applications in the field of nanotechnology, were carried out with a new methodology based on the principle of frequency change measurement. The first applications were made with the Differential Fabry-Perot Interferometer developed for these measurements [1].
As a continuation of this study, the TUBITAK UME Differential Fabry-Perot Interferometer, which was improved within the scope of the "EMRP JRP SIB08 subnano-traceability of sub-nm Length Measurements Project" [2], coordinated by Dr. Birk Andreas from the German Metrology Institute (PTB), and the X-ray interferometer developed by the UK Metrology Institute (NPL), were compared by performing interatomic distance measurements. TÜBİTAK UME research team succeeded in performing displacement measurements corresponding to the distance difference between silicon atoms with picometer accuracy.
Since 2013, the "SIB58 Angles Angle Measurements Project", coordinated by Assoc. Prof. Tanfer Yandayan from TÜBİTAK UME within the scope of the EU Framework Programs, has been developing angle measurement methods and new generation angle measurement devices for high-level scientific studies and technological applications [3].
The 1 nanoradian angular steps obtained with the precision small angle generator [4] developed at TÜBİTAK UME and improved within the scope of the SIB58 Angles Project were detected as a frequency change with the Differential Fabry-Perot Interferometer improved in the SIB08 subnano Project. The frequency-based angle measurement method, developed as a result of the joint work of TÜBİTAK UME project teams involved in the SIB08 subnano and SIB58 Angles projects, is important as an alternative to the methods used for angle measurements at the nanoradian level and below. To express what these measurable values mean; 1 nanoradian angle value symbolizes that a missile to be sent from Edirne to Hakkari can reach the target with an error of 1.5 mm at a flight range of 1500 km, while the measurement at the picoradian level symbolizes that the error of 1.5 mm to the target can be detected with a sensitivity of one thousandth.
The information obtained and produced is expected to meet the angular measurements at the nanoradian and picoradian level that arise as a need with developing technology, such as the angular adjustments of mirrors and optics used in space studies by institutions such as NASA, the production of mirrors used in the guidance of X-rays in accelerator centers such as CERN, and the study of the structure of matter using gamma rays. It is also expected to meet the high-level demands for reference standards in nanoradian angle metrology for the development of next-generation angle measurement devices and the improvement of existing ones.
References
1. M. Celik, R. Hamid, U. Kuetgens and A. Yacoot, Picometer displacement measurements using a differential Fabry-Perot optical interferometer and an x-ray interferometer, Meas. Sci. Technol. 23, 085901 (6pp) (2012)
2. https://www.ptb.de/emrp/subnano-home.html
3. http://www.anglemetrology.com
4. Yandayan T, Ozgur B, Karaboce N, and Yaman O, "High precision small angle generator for realization of the SI unit of plane angle and calibration of high precision aucollimators" Meas. Sci. Technol. 23 (2012), 094006